Kinesiology Tape for Pain Relief: A Natural Alternative to Medication?

Millions of people seek relief from muscle and joint pain every day. Whether it's from sports, injuries, posture-related strain, or chronic conditions, pain can disrupt daily life and limit movement. Many are now turning to kinesiology tape for pain relief as a non-invasive, drug-free option. But does it really work?
In this article, we will explore:
-
How kinesiology tape helps relieve pain
-
Common pain conditions it is used for
-
Scientific evidence supporting its use
-
Application techniques for specific types of pain
-
When to use it and when to seek professional care
🔍 What Is Kinesiology Tape and How Does It Relieve Pain?
Kinesiology tape is a stretchy, breathable, adhesive tape designed to mimic the skin’s elasticity. When applied correctly, it interacts with the body’s sensory and neuromuscular systems to provide a variety of therapeutic effects.
Key Pain Relief Mechanisms:
-
Decompression of Tissues
The tape lifts the skin microscopically, reducing pressure on underlying muscles, nerves, and lymph vessels. This promotes better circulation and reduces inflammation, both of which are key contributors to pain. -
Neurological Input
Pain signals are sent from nerve endings in the skin to the brain. Kinesiology tape stimulates these receptors, which can "distract" or override pain signals. This is known as the gate control theory of pain. -
Support Without Restriction
Unlike traditional athletic tape, kinesiology tape allows full range of motion while providing support. This can reduce the strain on injured tissues during movement, leading to less discomfort during recovery. -
Improved Lymphatic Drainage
By lifting the skin, the tape can create channels for lymph fluid to drain more efficiently, helping reduce swelling and pain associated with injury or inflammation.
✅ Top Pain Conditions Treated with Kinesiology Tape
Kinesiology tape is commonly used for both acute and chronic pain conditions, including:
| Pain Condition | Common Tape Application Areas |
|---|---|
| Lower back pain | Lumbar spine, paraspinal muscles |
| Neck pain | Upper trapezius, cervical spine |
| Shoulder pain | Rotator cuff, deltoid, scapular area |
| Knee pain | Patella, quadriceps, IT band |
| Plantar fasciitis | Arch of foot, heel |
| Elbow pain (e.g. tennis elbow) | Lateral or medial epicondyle |
| Wrist pain | Extensor or flexor tendons |
| Hip pain | Gluteus medius, tensor fascia latae |
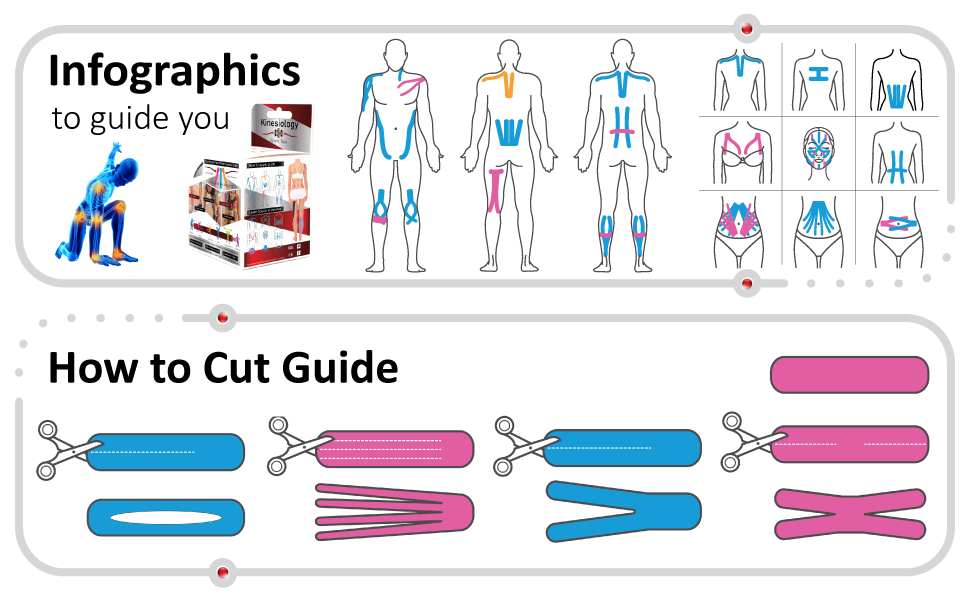
🧠 How to Apply Kinesiology Tape for Pain Relief
Proper application is crucial to achieve pain relief. Tape must be applied with appropriate tension, direction, and body positioning.
General Guidelines:
-
Clean, dry skin is essential before taping.
-
Use minimal stretch (10 to 25 percent) when targeting pain points.
-
Anchor the tape with no tension at the start and end.
-
Round tape edges to prevent peeling.
Example Techniques:
1. Lower Back Pain
-
Apply two vertical I-strips parallel to the spine, starting at the sacrum and ending below the ribcage.
-
Use a third horizontal strip across the lower back to support the paraspinal muscles.
-
Use light to moderate tension (15 to 25 percent).
2. Shoulder Pain
-
Use a Y-strip along the deltoid muscle, anchoring at the shoulder joint and spreading the tails across the front and back of the shoulder.
-
Add an I-strip diagonally across the rotator cuff if needed.
-
Stretch should be minimal in pain-sensitive areas.
3. Knee Pain (Patellofemoral Syndrome or Runner’s Knee)
-
Apply a strip below the kneecap, curving it around both sides to create a sling effect.
-
Use another strip vertically along the quadriceps to reduce load on the patella.
-
Keep tension light and focus on structural support.
📚 What Does the Research Say About Pain Relief?
While kinesiology tape is widely used, it is important to separate fact from hype.
Supporting Evidence:
-
A 2022 meta-analysis in the Journal of Orthopaedic & Sports Physical Therapy concluded that kinesiology tape provides short-term pain relief in conditions like knee osteoarthritis, lower back pain, and rotator cuff tendinopathy when combined with exercise or physical therapy.
-
Another study in the British Journal of Sports Medicine found that kinesiology tape significantly improved pain perception and range of motion in individuals with chronic neck pain.
-
Research shows its effectiveness is likely due to the sensorimotor stimulation, improved lymphatic flow, and patient expectation (placebo effect can be a factor in pain management).
Limitations:
-
Effects are often temporary and most beneficial in the first 72 hours.
-
Tape is not a replacement for physical rehabilitation or medical treatment in serious conditions.
-
Individual results vary based on tape quality, application skill, and underlying condition.
⚠️ When Not to Use Kinesiology Tape for Pain
Although generally safe, avoid taping in the following situations:
-
Open wounds or irritated skin
-
Known tape allergies or skin sensitivities
-
Deep vein thrombosis or vascular disorders
-
Unexplained or severe pain not diagnosed by a healthcare provider
-
Fractures or dislocations
Always consult a qualified therapist or physician before taping in the presence of serious or persistent pain.
🏁 Final Thoughts: Can Kinesiology Tape Replace Painkillers?
Kinesiology tape is not a cure for pain, but it offers a non-invasive, drug-free alternative that many find helpful for reducing discomfort and improving mobility. It is especially useful as part of a broader pain management plan that includes:
-
Targeted exercises
-
Manual therapy or physiotherapy
-
Ergonomic adjustments
-
Stretching and mobility work
-
Adequate hydration and rest
For individuals looking to avoid or reduce pain medication, kinesiology taping may be a valuable tool in your self-care routine.
🧩 SEO Summary:
Keywords Targeted: kinesiology tape pain relief, how to use kinesiology tape for pain, tape for back pain, tape for knee pain, non-medication pain relief, kinesiology tape application, natural pain relief methods
Meta Description: Discover how kinesiology tape offers a natural solution for pain relief. Learn taping techniques for common pain conditions and find out what science says about its effectiveness.